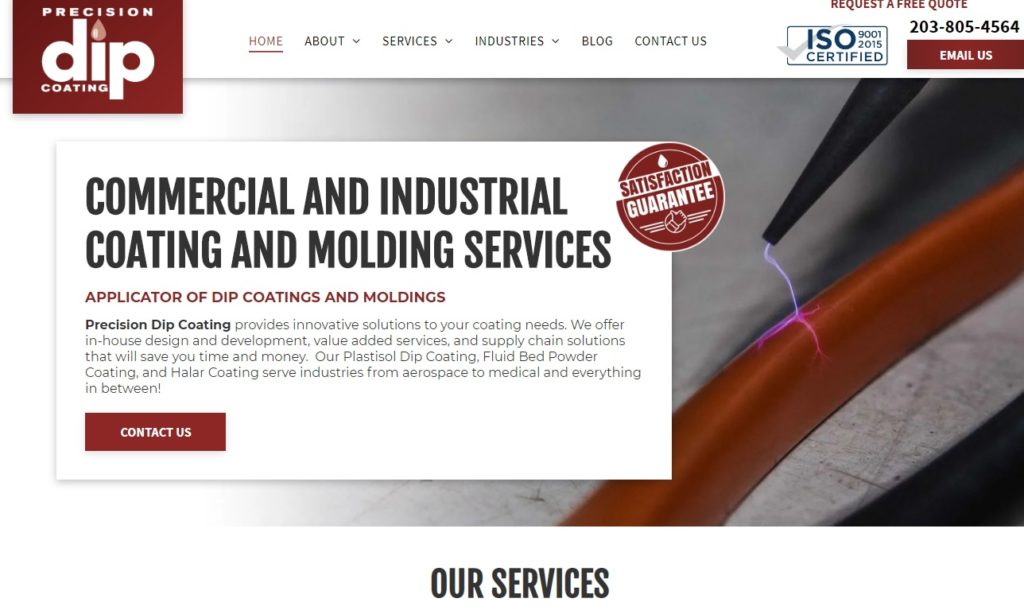
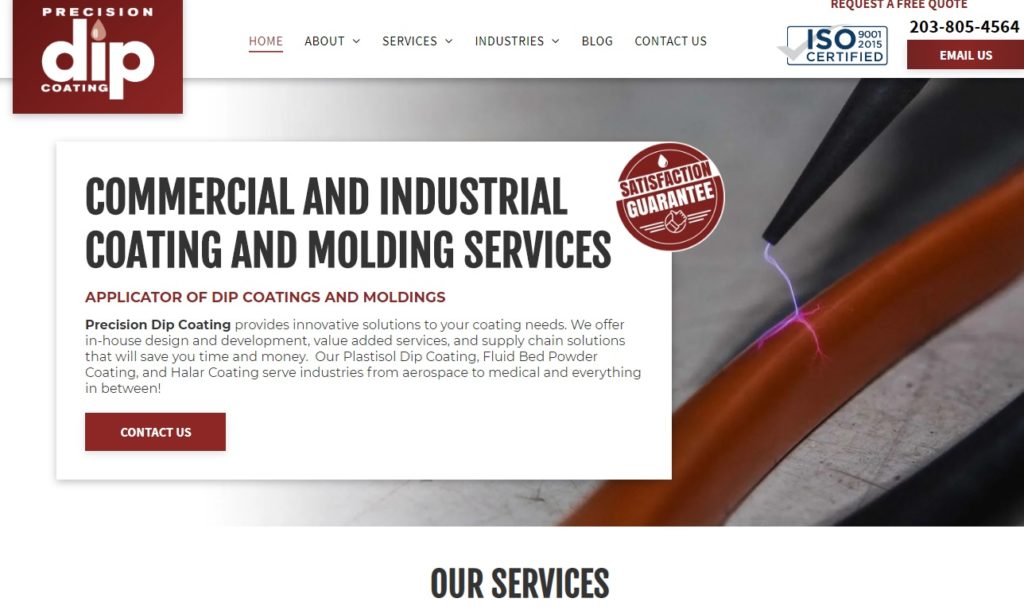
There are several methods for plastic dip coating that include: hot dip coating in a fluidized bed of polymer powder, hot dip coating a product in a vinyl plastisol, and spraying polymer powder on a heated product. The method that is used usually depends on the needs of the product being created or the metal being treated. Read More…
Precision Dip Coating provides dip coating services for the manufacture of soft plastic parts such as cap plugs. hand grips, and more. Decorative and protective, our services are very cost effective and we have a proven track record for on time delivery and precise manufacturing. We can match any color you need, and offer services such as assembly, die cutting, packaging, and decorating.
Carlisle Plastics is a dip molding plastics manufacturer offering end caps, plastisol paint masks, thread protectors, tube closures, protective caps and decorative caps.

At Production Sciences, Inc., we pride ourselves on being pioneers in the realm of dip-molded plastics, sculpting a legacy of innovation and excellence that spans decades. As a collective force, we embody a commitment to precision, creativity, and unwavering quality in the realm of plastic manufacturing.

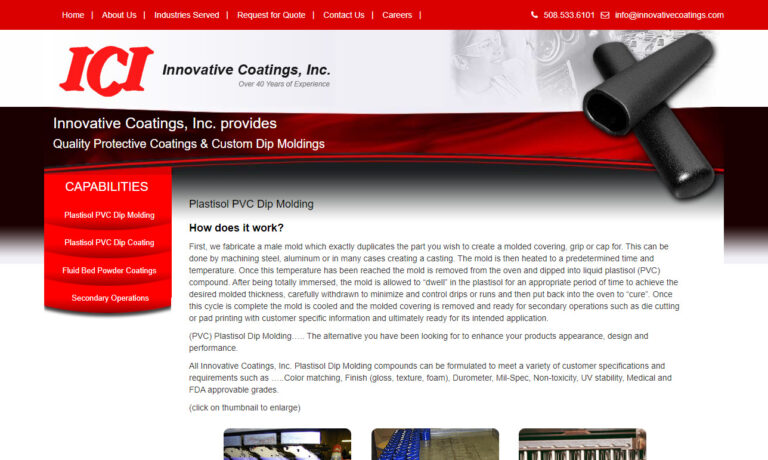
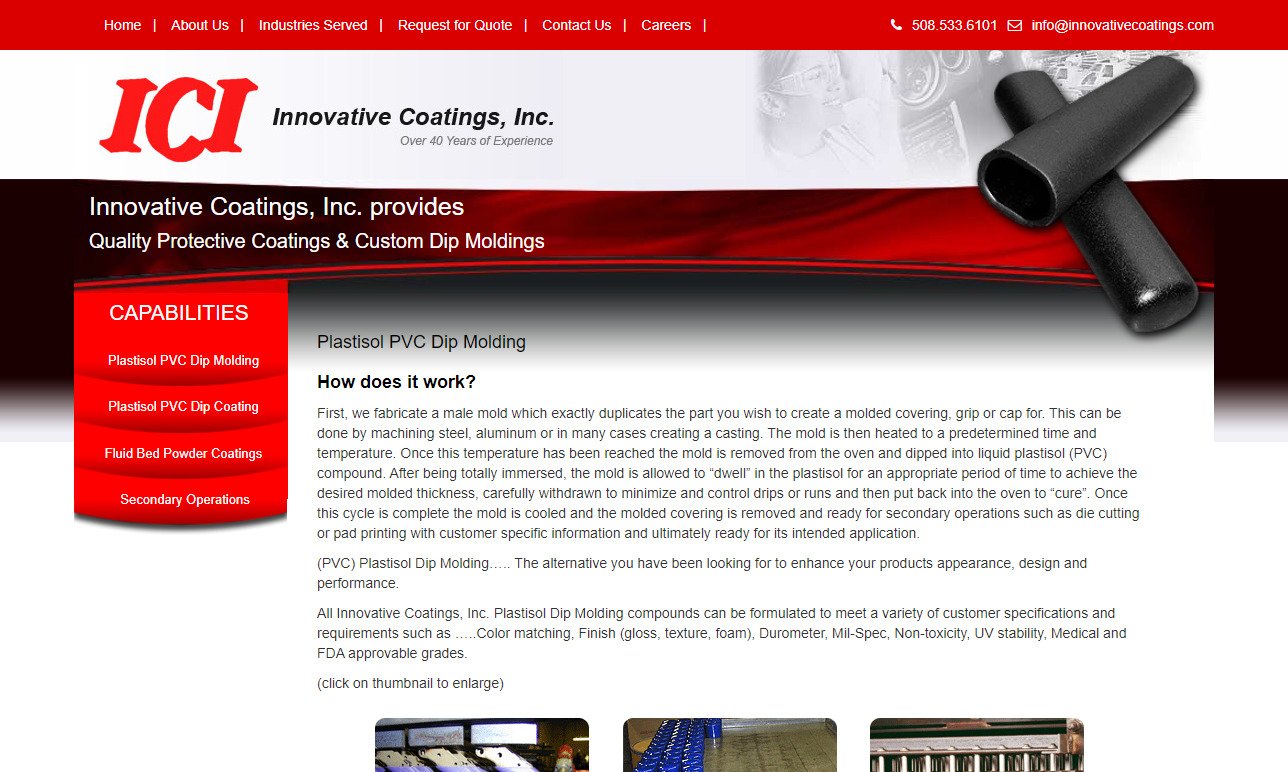
Innovative Coatings is a manufacturer of plastisol dip molding and fluidized bed powder coatings of epoxy, polyolefins, nylon and vinyl. Our dip coatings are of FDA-approved and biomedical grades.
More Plastic Dip Coating Companies
Hot Dip Coating: Comprehensive Guide to Polymer Powder and Plastisol Applications
Hot dip coating is a widely used industrial process for applying a durable, protective, and aesthetically pleasing plastic layer to metal substrates. This advanced coating method utilizes either a fluidized bed of polymer powder or a liquid bath of vinyl plastisol to create a uniform, corrosion-resistant finish across a variety of metal products. Hot dip coating is a crucial technique within the industrial coatings sector, delivering superior performance for applications demanding robust metal protection. Understanding the intricacies of hot dip coating, from substrate preparation through to application and the multifaceted benefits, is essential for manufacturers, engineers, procurement professionals, and buyers seeking reliable solutions for metal protection and product longevity.
What Is Hot Dip Coating?
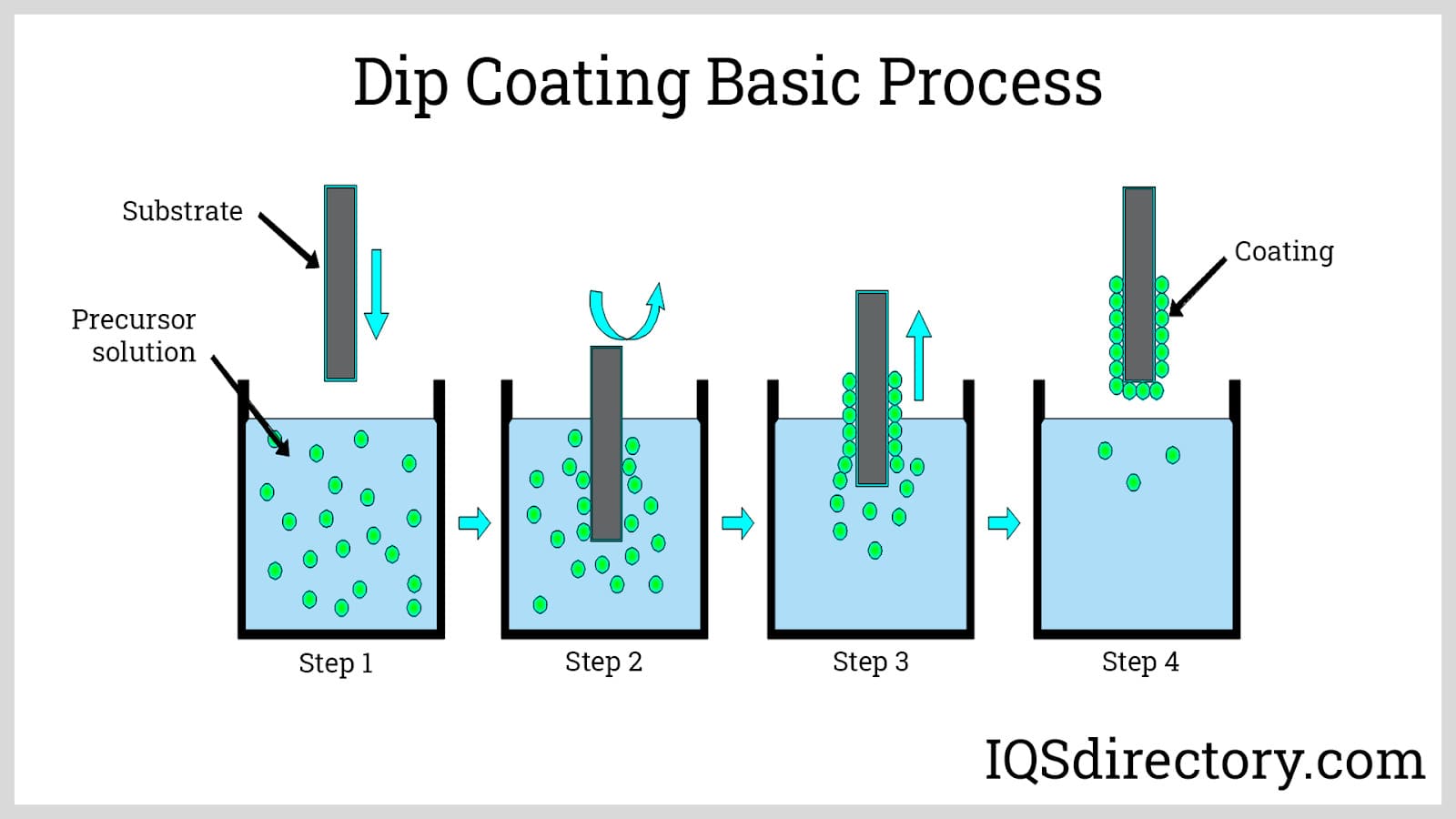
Hot dip coating, also referred to as plastic dip coating, polymer dip coating, or polymer powder coating, is a thermal process in which a preheated metal component is immersed in a fluidized bed or a liquid bath containing plastic material. The plastic—typically a thermoplastic polymer powder or a vinyl plastisol—melts and forms a continuous, adherent coating over the metal surface. This method is renowned for its efficiency, versatility, and exceptional corrosion protection, making it a preferred choice in industries ranging from automotive manufacturing and electronics to healthcare, construction, marine, and consumer goods.
Are you searching for the most effective metal coating technology for your specific application? Explore the key differences between hot dip coating, electroplating, and powder coating to determine which offers the best balance of durability, cost, and appearance.
How Does Hot Dip Coating Work? Exploring the Process
To achieve a high-quality, plastic-coated metal finish, the hot dip coating process involves several critical steps, all of which impact the final product's protective capabilities and appearance. Let’s break down the standard workflow:
- Surface Preparation: The metal substrate is thoroughly cleaned, degreased, and often pre-treated with a chemical solution or abrasive blasting. This step removes oils, oxides, and contaminants, ensuring the optimal adhesion of the plastic coating. High-quality surface preparation is essential for maximizing the coating's longevity and corrosion resistance.
- Preheating: The cleaned metal part is placed in an industrial oven and heated to a precise temperature, typically between 300°F and 800°F (150°C to 425°C), depending on the polymer material. Preheating activates the surface and facilitates immediate melting and flow of the polymer upon contact.
- Coating Application: Several methods can be used, each tailored to the geometry and end-use of the component:
- Fluidized Bed Dip Coating: The hot metal is immersed in a fluidized bed of polymer powder, such as polyethylene, nylon, or epoxy. The powder melts on contact, fuses to the metal, and forms a uniform coating layer. This technique is especially effective for parts requiring thick, pinhole-free coverage.
- Vinyl Plastisol Dip Coating: The object is dipped into a liquid bath containing suspended PVC particles. The heat from the substrate causes the vinyl plastisol to gel and bond to the metal. This method is ideal for achieving soft-touch finishes and custom textures.
- Flock Spraying (Electrostatic Spray Coating): For large, irregular, or intricately shaped components, polymer powder is sprayed onto the preheated surface. Electrostatic charges may be used to enhance coverage and improve adhesion, enabling efficient coating of large production batches.
- Curing and Cooling: After application, the coated part is either air-cooled or placed in a curing oven. This step ensures that the plastic fully melts, flows, and solidifies, providing a smooth, defect-free finish. Proper curing maximizes adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance.
- Inspection and Quality Control: The final product undergoes visual and mechanical inspections to verify coating thickness, adhesion strength, and surface uniformity. Many suppliers employ digital thickness gauges, impact testers, and standardized visual inspections to ensure compliance with industry standards and customer specifications.
Curious about how to optimize your hot dip coating process for specific performance requirements? Ask these questions: What thickness do I need for my coating? Which polymer type offers the best resistance for my operating environment? How does surface preparation impact adhesion and durability?
Key Benefits of Hot Dip Coating for Metal Protection
Why choose hot dip coating over alternative metal finishing methods such as powder coating, electroplating, or galvanizing? Hot dip polymer coatings provide an array of technical and economic advantages, making them the go-to solution for many industrial and commercial applications:
- Exceptional Corrosion Resistance: The plastic layer acts as a robust barrier, preventing water, chemicals, and atmospheric gases from contacting the metal substrate. This greatly reduces the risk of rust, oxidation, and long-term degradation—even in harsh or marine environments.
- Electrical Insulation: Polymers such as PVC and nylon are natural electrical insulators, making hot dip coating an excellent choice for electrical and electronic components that require dielectric protection or environmental sealing.
- Impact and Abrasion Protection: The flexible, resilient coating absorbs shocks and resists scratches, minimizing mechanical damage during handling, shipping, installation, and end-use. This property is particularly valuable for tools, hardware, and structural components exposed to heavy wear.
- Enhanced Grip and Comfort: Hot dip coatings can be engineered with soft-touch surfaces or custom textures, greatly improving the ergonomics of hand tools, handles, sporting goods, and consumer products. Enhanced grip also contributes to user safety and product satisfaction.
- Customizable Appearance: Manufacturers can specify a wide range of colors, gloss levels, surface finishes, and thicknesses to meet branding, aesthetic, and functional requirements. The process also allows for custom color matching and decorative effects.
- Cost-Effective Manufacturing: Dip coating is efficient for both high-volume and custom production runs, reducing labor and material waste compared to painting or electroplating. The process supports high throughput and rapid changeovers.
- Seamless, Pinhole-Free Coverage: Unlike spray paints, the immersion process yields a uniform, continuous layer—even on complex geometries, sharp edges, and hard-to-reach areas. This ensures reliable long-term protection and visual appeal.
- Chemical Resistance: Many hot dip polymers exhibit strong resistance to acids, alkalis, solvents, and oils, making them ideal for industrial, automotive, and laboratory environments.
- UV and Weather Resistance: Specialized formulations can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, rain, and temperature extremes, resulting in lasting color stability and mechanical properties.
Trying to determine which metal finishing process best meets your requirements for corrosion resistance, appearance, and cost? Compare hot dip coating with powder coating, anodizing, and plating for a detailed analysis.
Common Hot Dip Coating Applications
Hot dip coatings are integral to a wide spectrum of industries and use cases. Explore some of the most common applications and consider how your products could benefit from advanced plastic coating technologies:
- Hand Tools and Grips: Screwdrivers, pliers, wrenches, and garden tools receive comfortable, slip-resistant coatings that improve user safety, reduce hand fatigue, and extend product longevity.
- Toys and Recreational Equipment: Playground structures, sports gear, and children’s toys are protected against weathering, UV exposure, and physical abuse, meeting stringent safety and durability standards.
- Medical Instruments: Surgical scissors, forceps, and diagnostic tools are coated for enhanced sterility, corrosion protection, and ease of cleaning. Medical-grade polymers can be selected for biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility.
- Electrical Equipment: Terminal covers, circuit boards, cable connectors, switchgear, and enclosures benefit from electrical insulation, abrasion resistance, and environmental sealing.
- Plumbing Fittings: Pipe clamps, brackets, and fixtures are protected from moisture and chemical corrosion in demanding plumbing and HVAC environments.
- Automotive Components: Battery trays, brackets, underbody parts, springs, and fasteners receive rustproof coatings that withstand harsh road conditions, deicing salts, and abrasives.
- Architectural and Construction Products: Fencing, railings, balustrades, fasteners, and outdoor furniture are coated for visual appeal, color durability, and extended service life.
- Industrial Racks and Storage Systems: Wire shelving, baskets, and trolleys are protected against abrasion, corrosion, and chemical attack—ideal for food processing, warehousing, and laboratory settings.
- Marine Hardware: Boat fittings, dock equipment, and underwater structures benefit from saltwater-resistant polymer coatings that prolong service life.
Wondering if hot dip coating is suitable for your application? Ask: What are the main environmental and mechanical stressors my component will face? What industry standards or certifications must the coating meet?
Types of Polymer Powders and Plastisols Used in Dip Coating
Choosing the right polymer for your dip coating application is essential to achieving the desired performance characteristics. The material selected directly impacts the coating’s chemical resistance, mechanical properties, and suitability for specific environments. Here are the most popular materials used in hot dip coating:
- Polyethylene (PE): Offers excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and low-temperature impact strength. It is commonly used for wire coatings, automotive parts, and consumer goods requiring moisture and abrasion resistance.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Available in both powder and plastisol forms, PVC is valued for its electrical insulation, flame resistance, cost-effectiveness, and wide color palette. It is prevalent in tool grips, electrical housings, and outdoor furniture.
- Nylon (Polyamide): Provides superior abrasion resistance, low friction, and high mechanical strength. Nylon coatings are ideal for mechanical components, industrial racks, conveyor rollers, and automotive hardware where wear resistance is critical.
- Polypropylene (PP): Selected for its good chemical resistance, high temperature stability, and lightweight properties in industrial and laboratory equipment.
- Epoxy Powders: Deliver outstanding corrosion protection, chemical resistance, and adhesion, often used for outdoor, marine, and heavy industrial applications where environmental exposure is severe.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Create soft-touch, flexible surfaces for consumer products, hand tools, and medical devices that require ergonomic design and comfort.
- Specialty Polymers: Advanced options include fluoropolymers (PTFE, FEP, PFA), polyether ether ketone (PEEK), and high-performance blends for extreme chemical, thermal, or UV resistance.
Looking to select the best polymer for your industry or product? Consider: What operating temperatures and chemicals will the part encounter? Is a soft-touch or rigid finish preferred? What are the color and thickness requirements?
Hot Dip Coating vs. Alternative Metal Finishing Methods
How does hot dip coating compare to other metal finishing and coating technologies? Here’s a quick overview of the alternatives and why hot dip remains the preferred choice for many buyers and specifiers:
- Electroplating: Adds a thin metallic layer (e.g., zinc, nickel, chrome) for conductivity and corrosion resistance. However, electroplating lacks the impact, abrasion, and dielectric protection of polymer coatings and cannot provide soft-touch or textured surfaces.
- Powder Coating: Involves electrostatic spraying of dry powder, which is then cured. While similar to fluidized bed coating, traditional powder coating may not achieve the same thickness, flexibility, or pinhole-free coverage—especially for complex or three-dimensional shapes.
- Spray Painting: Fast and economical for large surfaces, but prone to pinholes, uneven coverage, and lower durability compared to immersion-based polymer coatings. Solvent-based paints may also pose environmental and health concerns.
- Galvanizing: Applies a zinc layer for corrosion protection, commonly used in construction. It offers strong rust prevention but does not provide the color, texture, tactile, or electrical insulation benefits of plastic coatings.
- Anodizing: Used for aluminum, anodizing creates a hard, corrosion-resistant oxide layer but is limited by substrate compatibility and appearance options.
Still unsure which process best fits your needs? Ask: Does my application require electrical insulation, chemical resistance, or a decorative finish? Which process offers the best total cost of ownership for my product lifecycle?
Frequently Asked Questions About Hot Dip Coating
- What factors determine the best hot dip coating process for my application?
Consider the size, geometry, and surface area of your components, required coating thickness, environmental exposure (e.g., chemicals, UV, salt spray), mechanical stresses, and any regulatory or safety requirements. Consult with a polymer coating specialist to specify the optimal material and process for your needs. - How thick can dip-coated plastic layers be?
Typical thicknesses range from 0.2 mm (8 mils) up to several millimeters, depending on immersion time, polymer type, and heating temperature. Multiple layers can be applied for added protection or specific tactile properties. - Are hot dip coatings suitable for outdoor or marine environments?
Yes—materials like nylon, epoxy, and PE are highly resistant to UV, salt spray, and weathering, making them ideal for harsh outdoor service. Custom formulations can further enhance performance in challenging environments. - Can I customize the color and finish of my hot dip coated products?
Absolutely. Manufacturers offer a broad palette of colors, surface textures (smooth, matte, textured), and gloss levels to match branding, design, or functional needs. - Is hot dip coating environmentally friendly?
Many modern polymers are formulated to be low-VOC, non-toxic, and recyclable. The process minimizes waste, and the durability of the coating reduces replacement rates and environmental impact over the product’s lifecycle. - What are the typical lead times for hot dip coating services?
Lead times vary by provider and order volume but can range from a few days for small runs to several weeks for complex, high-volume projects. Early engagement with your supplier can help ensure timely delivery. - What certifications and quality controls should I look for?
Look for ISO 9001, RoHS, REACH, and industry-specific certifications to guarantee process consistency, regulatory compliance, and high product quality.
Buyer’s Guide: How to Choose a Hot Dip Coating Provider
When sourcing plastic coating services for your metal components, keep these decision factors in mind to ensure optimal results and long-term value:
- Technical Expertise: Look for providers with extensive experience in your application sector—whether automotive, medical, industrial, or consumer products—and deep knowledge of polymer chemistry, process control, and quality assurance.
- Material Selection: Partner with companies offering a wide selection of polymers, colors, and finishes, with the ability to provide custom formulations as needed for unique requirements.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the provider can handle your volume needs, from prototypes and pilot runs to large-scale manufacturing, with fast turnaround times and flexible scheduling.
- Quality Certifications: Verify ISO 9001, RoHS, REACH, ASTM, and other relevant certifications to guarantee process consistency, regulatory compliance, and international acceptance.
- Value-Added Services: Consider additional offerings such as design assistance, rapid prototyping, secondary operations (e.g., drilling, assembly, laser marking), and just-in-time delivery for supply chain efficiency.
- Customer Support and Communication: Choose a supplier with responsive technical support, transparent pricing, clear project management, and a track record of positive customer feedback.
- Case Studies and References: Ask for examples of similar projects or applications, along with customer testimonials, to assess the provider’s expertise and reliability.
Ready to connect with leading plastic dip coating vendors? Search for top-rated polymer coating companies and compare their capabilities, case studies, and customer reviews to make an informed sourcing decision.
Hot Dip Coating Process: Step-by-Step Overview
- Surface Cleaning: Remove oils, dirt, and rust using solvents, abrasive blasting, or chemical cleaning to prepare the metal for optimal coating adhesion and performance.
- Preheating: Heat the part to the recommended temperature for your selected polymer, ensuring rapid melting and flow during coating application.
- Coating Application: Dip or spray the plastic material onto the hot surface, ensuring even, complete coverage and desired thickness.
- Curing: Allow the coated part to cool and cure fully, either at ambient temperature or in a controlled oven, depending on the polymer system.
- Inspection: Check for coating uniformity, adhesion, surface defects, and thickness using visual inspections and digital measurement tools.
- Packing and Shipping: Package the finished components to prevent damage during transport, ensuring coatings remain pristine upon delivery.
Explore Further: Related Processes and Advanced Applications
Interested in learning more about advanced metal finishing and polymer coating technologies? Consider these related topics to expand your knowledge and make better-informed purchasing decisions:
- Electrostatic Powder Coating: How does it work, and when should you choose it over hot dip processes for flat panels, enclosures, or decorative finishes?
- Liquid Epoxy Coatings: Benefits for corrosion protection in pipelines, storage tanks, marine hardware, and industrial plant equipment.
- Insert Molding and Overmolding: Combining metal and plastic in a single part for added functionality, durability, or ergonomic improvement in high-performance products.
- High-Performance Polymers: Explore PTFE, PEEK, and fluoropolymer coatings for extreme chemical, thermal, or frictional environments where conventional coatings may fail.
- Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Coating Options: Discover innovations in low-VOC, recyclable, and bio-based polymer coatings for green manufacturing initiatives.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Learn about ASTM, ISO, and sector-specific requirements for coated products in automotive, medical, electrical, and food-contact applications.
Get Started: Request a Quote or Consultation
Ready to enhance your products with advanced hot dip coating solutions? Whether you need protective coatings for hand tools, medical devices, automotive parts, outdoor structures, or custom industrial equipment, finding the right partner is essential for project success. Request a quote or schedule a consultation with leading polymer coating specialists today. Discuss your specific project requirements, desired performance attributes, and any regulatory or compliance considerations for optimal results.
Summary: Why Hot Dip Coating Is the Best Choice for Metal Protection
Hot dip coating offers unmatched durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness for protecting metal parts in diverse industries. By leveraging cutting-edge polymer chemistries and precision application methods, manufacturers can achieve long-lasting, attractive, and functional finishes that outperform traditional metal plating and painting. From advanced corrosion prevention and electrical insulation to improved product ergonomics and appearance, the benefits of hot dip coating are clear—making it the smart choice for buyers, engineers, and product designers alike. The process supports a wide range of applications, from automotive and medical to construction and consumer goods, ensuring lasting value and performance.
Have more questions about hot dip coating, metal finishing solutions, or polymer selection? Contact a specialist today or explore our resources for in-depth guides, case studies, and expert insights into optimizing your metal protection strategy.





 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators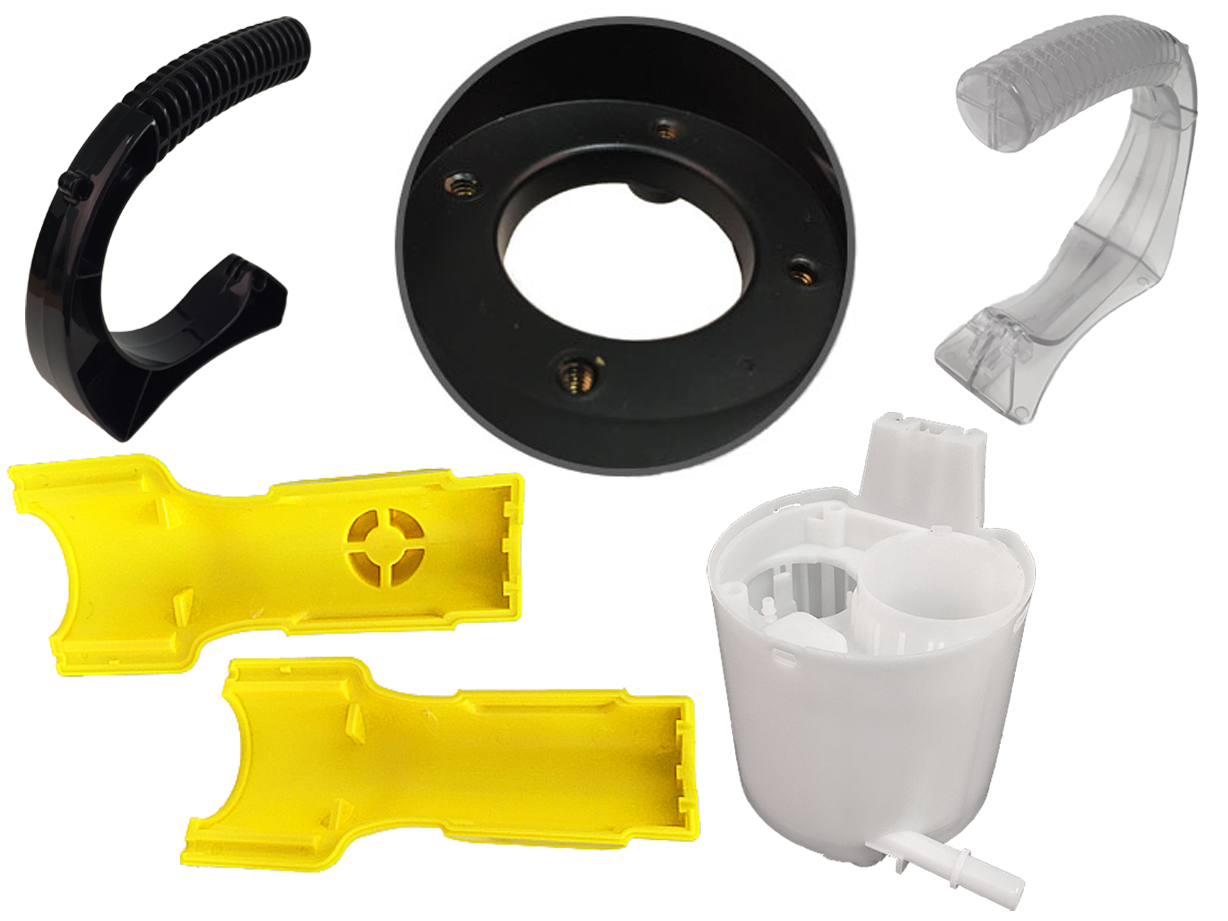 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics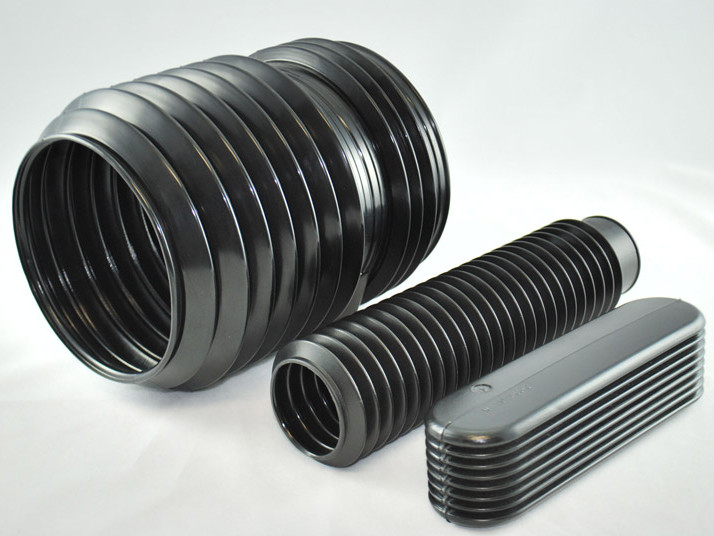 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services